A Complete Guide to College Entrance Examinations In india 2025
At the time of completing 12th class in India, the candidates are confronted with the challenge of dealing with entrance examinations for admission to higher education. They are national and state-level exams in engineering, medical, law, and liberal arts. Students must be aware of the different entrance exams in India to decide about their academic future. This entrance exam guide would provide complete information about exam patterns, eligibility criteria for admission, and ways of preparing for students and parents who intend to make a career pathway for study after post-secondary education.
What Are Entrance Exams & Why They Matter
Entrance exams in India after 12th serve as standardised evaluation mechanisms for college admissions across the country. These examinations hold merit-based selection for various undergraduate courses, conferring degrees at both government and private institutions. Major exams like CUET UG, JEE Main, and NEET-UG are conducted by the National Testing Agency (NTA), while several states conduct their regional testing systems.
- Merit-based Selection: The entrance examination level provides equal evaluation criteria among applicants from various educational boards. This will make the competition fairly balanced despite the academic differences in the region.
- Cut-off Determination: Examination scores directly influence admission cut-offs for specific colleges and courses, with top-scoring candidates gaining access to premier institutions and scholarship opportunities.
- Mandatory Admission Criteria: Central universities, IITs, NITs, and AIIMS require mandatory entrance exam qualifications, making these tests essential for accessing quality higher education.
Major List of Entrance Exams After 12th in India
The entrance exam in Indian system encompasses the national-level examination conducted by the central agencies and specialised examinations for professional courses.
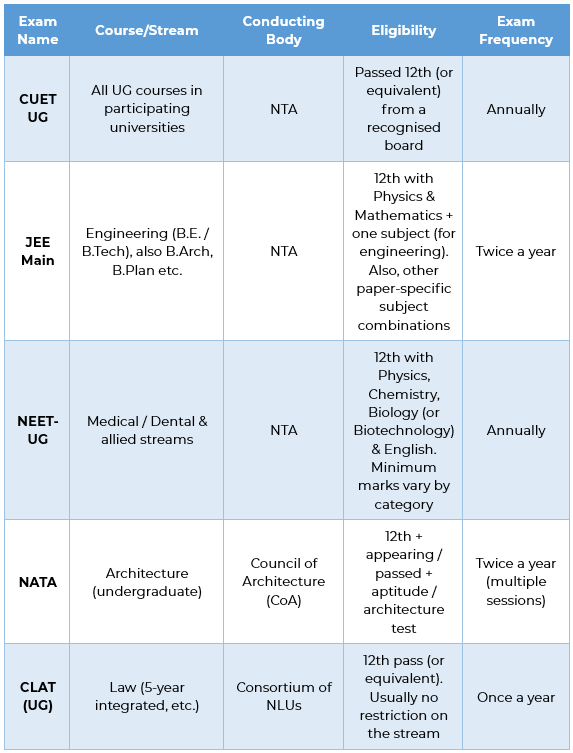
Stream-Specific Entrance Exam Requirements
Different entrance exams in India cater to specific academic streams and subject combinations from 12th standard. Students of science stream have the biggest variety of professional entrance examinations. Commerce and arts students have rather field-specific testing.
- Science Stream Requirements: The candidate must have passed JEE Main with Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics as compulsory subjects, with minimum marks in the 12th standard for joining IIT.
- Medical Stream Preparation: NEET-UG candidates require Physics, Chemistry, and Biology as subjects with practicals attached to them to compete for MBBS seats in India.
- Architecture Pathway: NATA and JEE Paper-II candidates need strong mathematical foundations and drawing aptitude, with some institutions requiring portfolio submissions alongside examination scores.
- Law and Liberal Arts: CLAT-UG and CUET examinations assess English comprehension, logical reasoning, and general knowledge rather than specific subject expertise from 12th standard.
- Commerce and Management: The Commerce exams under CUET and commerce entrance tests of universities test the candidate’s mathematical abilities, working knowledge of English, and analytical reasoning. These are exams for admission to business administration programmes.
Easiest Entrance Exam in India Analysis
The concept of “easy entrance exams in India” depends on multiple factors, including competition ratio, syllabus complexity, and individual preparation strengths. Students should evaluate examinations based on their academic profile rather than perceived difficulty levels.
- Lower Competition Ratios: Private university examinations like KIITEE, COMEDK, and PESSAT have fewer applicants per seat compared to JEE Main or NEET, creating better admission probabilities.
- Simplified Syllabus Coverage: State-level examinations cover exclusively the NCERT curriculum, not advanced issues found in national-level exams, which makes the preparation simpler for average students.
- Multiple Attempt Opportunities: Examinations like BITSAT and VITEEE offer multiple test dates and rescheduling options, allowing students to improve their performance through repeated attempts.
- No Negative Marking Systems: Some tests reject any form of negative marking against the wrong answers to encourage the students to have all questions answered without being penalised, thereby obtaining better scores.
- Regional Language Options: State examinations provide question papers in regional languages alongside English, benefiting students more comfortable in their native languages.
Timeline and Important Examination Dates
Strategic positioning around examination dates surely prevents missed opportunities or an appropriate preparation status. Major entrance examinations follow predictable annual calendars with specific application and testing windows.
- Procedures for the Application Period: Most of such national examinations accept applications between December and March; however, some, like JEE Main, start earlier, i.e., for a January attempt. Students must prepare their documents, such as photographs, signatures, and academic certificates in advance.
- Syllabus Publication Schedule: Conducting bodies release detailed syllabi and specimen papers, some months prior to the exams. This provides students with a proper roadmap for preparation on a structured basis.
- Preparation Duration Requirements: Engineering entrance examinations usually demand one to two years of focused study, while medical examinations require longer preparation because of the wider syllabus.
- Result and Counselling Timeline: Results are generally released within two to six weeks of the exam, followed by counselling processes that may extend over two to three months until final seat allotments are confirmed.
- Academic Year Alignment: Most entrance examinations are conducted between April and June, with admissions beginning around July and August, in line with the Indian academic calendar.
Strategic Preparation and Examination Selection
Successful entrance examination performance requires systematic preparation approaches and intelligent selection of target examinations based on individual capabilities and career aspirations.
- Complete Syllabus Analysis: Students must thoroughly understand examination patterns, marking schemes, and topic weightages before beginning preparation, focusing effort on high-scoring sections.
- Previous Years’ Paper Practice: Regular practice with past examination papers develops time management skills and familiarity with question formats, improving performance confidence.
- Mock Test Integration: Weekly mock examinations under timed conditions help identify preparation gaps and build stamina for lengthy examination sessions.
- Subject Prioritisation Strategy: Students should allocate study time based on subject weightages and personal strengths, dedicating extra effort to challenging topics.
- Multiple Examination Planning: Applying for relevant examinations increases admission chances while avoiding overcommitment that dilutes preparation quality across too many tests.
- Financial Planning Consideration: Examination fees, coaching expenses, and travel costs for multiple tests require careful budget planning by families.
Conclusion
The entrance exam in India after 12th offers diverse pathways to quality higher education through national examinations like JEE, NEET, and CUET alongside specialised state and private university tests. Those who succeed in such a competitive atmosphere are well versed in the strategy of selecting examinations, methods of preparation, and the fair evaluation of their academic strengths. Early awareness of the examination requirements, steady preparation, and the backing of family constitute a strong base for success in India’s entrance exams. Parents can help by understanding exam logistics, supporting study routines, and guiding students in educational choices.
Frequently Asked Questions
1) Can students attempt multiple entrance examinations in the same year?
Students can register and give multiple entrance tests simultaneously, with most applying for relevant tests for admission opportunities. However, the dates of examinations clash with each other, leaving students to select which one to attend, depending on their institute of priority.
2) Is CUET replacing individual university entrance examinations in India?
CUET UG continues to be adopted by central, state, and private universities, which accept their scores. However, specialised examinations like JEE, NEET, and CLAT maintain independent operations alongside CUET.
3) What constitutes the minimum eligibility for JEE Main after 12th standard?
JEE Main requires 12th standard completion with Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics subjects, plus minimum aggregate marks for IIT admission eligibility through JEE Advanced.
4) Do commerce and arts students need specialised entrance examinations?
Commerce and arts students are primarily into UG programmes through CUET, but some courses require further tests. Entrances exist for individual courses such as journalism, design, and hotel management, which provide some sort of foundation for PG entrance examinations in respective fields.
5) Are free preparation resources available for entrance examinations?
Many free resources offer mock tests, video lectures, study material, and all of this is provided by government schemes, online portals, and truly educational websites. Most syllabi of various entrance exams are themselves on NCERT textbooks, and that too is available at a nominal price.


